Sexual Health
Contraception
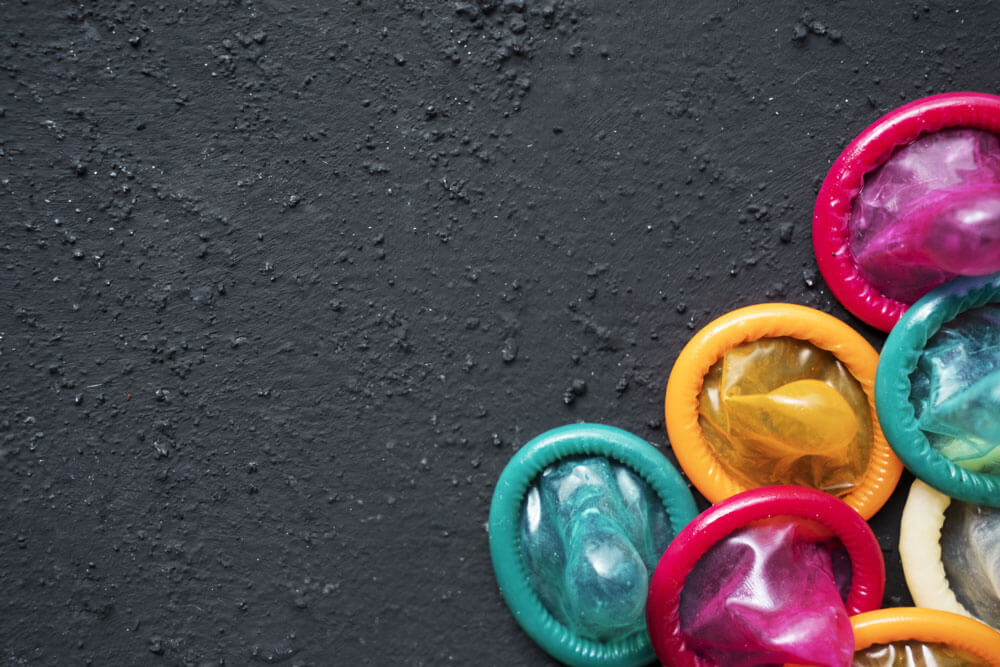

Contraception is a necessity today for sexually active people to carry on their lifestyle without any health or pregnancy risks. The most common forms of contraception include barrier methods, which prevent the sperm from mixing with the egg, and contraceptive pills, which prevent ovulation for a brief period in females. However, there are a number of other contraceptive methods as well to help achieve the same end. The common contraception methods for the 2 sexes include:
Men
Condoms: Condoms are the go-to contraceptive method for many. They are the only type of contraception that can protect against both pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Made of thin latex, condoms prevent pregnancy by stopping sperm from meeting the egg and if used correctly during vaginal, anal, and oral sex, they also protect against STIs.
Vasectomy: Vasectomy, aka male sterilization, is a surgical process which cuts or seals the tubes that carry a man’s sperm. The process is simple, takes about 15 minutes, and can be carried out under a local anesthetic. A vasectomy has no impact on the sexual drive of a man as he can still enjoy sex, experience erections and ejaculations. But with the tubes sealed off, the ejaculation doesn’t contain sperm and therefore, prevents pregnancy.
Women
Condom: A woman’s condom serves the same purpose – to avoid pregnancy and STIs by avoiding contact between the sperm and the egg. It is inserted into a woman’s vagina before having sex and consists of a soft, loose-fitting pouch, with a ring on each end. The ring inserted into the vagina holds the female condom in place while the ring at the other end (the open end) remains outside the vagina, helping keep the condom in place and also allowing easy removal.
IUD: An intrauterine device (IUD) is a long-term, reversible type of contraception and is regarded among the most effective reversible birth control methods. While it is indeed very good at preventing pregnancy, the same cannot be said for its effectiveness against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Another advantage of IUD is that it can be used for years at a time and a woman can get pregnant even immediately after it is removed.
Injectable contraception: The most common type of injectable contraceptive method in India is Depot-medroxy progesterone acetate (DMPA) – marketed in the country as Depo-Provera. It is given in a dose of 150 mg intra-muscularly every three months and is again an effective, long-term, and reversible method. However, this method also requires certain cautions, like the history of breast cancer, heart diseases, etc.
OCPs and ECPs: Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) and Emergency contraceptive pills (ECPs) are both birth control pills consumed to prevent unwanted pregnancy. While OCPs are consumed regularly, ECPs are taken within a limited timeframe after sex. Both OCPs and ECPs are readily available at medical stores, with Saheli, IPill, and Unwanted 72 being some of the most common examples.
All the contraception methods come with their pros and cons and it is for a couple to decide the one that suits their needs the best. An open discussion between the two about when they want to have children is necessary to figure out the most suitable method. Married couples usually prefer permanent methods after having the desired number of children while unmarried couples favour temporary methods since pregnancy needs to be avoided only till they are married.